NBIF Equipment
Meeting Facilities and Control
Meeting Facilities and Control
Meeting Facilities and Control
Visualisation Suite
NBIF has a Teams enabled small meeting room for 8-10 visitors, which allows collaborative working with four screens. This enables researchers and industry, who are not based in NBIF, to fully engage in the experiments.
The Visualisation Suite also houses the DAFNI computer, which is a high spec workstation has 32 cores AMD processors with an NVIDIA GeoForce RTX 2080 GPU and 256 GB RAM that allows users to run large simulations on local machines but also can be linked to DAFNI computing services to provide additional computing resources.
Several software packages are installed, including COMSOL Multiphysics, ABAQUS, SolidWorks, and AutoCAD in addition to all other standard packages.
Control Room
A control room overlooking the test hall which is where the hydraulic systems are controlled, such as the loading actuators and the moveable floor. It is also where the CCTV facilities that cover the main test hall are controlled.
Knowledge Transfer Office
We have a knowledge transfer office available for visiting researchers and industry to use during collaborative research enabling visitors to continue with their day-to-day commitments while based at NBIF.
Material Characterisation Lab
Material Characterisation Lab
Advanced Dynamic Triaxial
A triaxial that can act in the ‘traditional’ compressive format or as a dynamic system (38 mm, 50 mm and 100 mm diameter samples).
Dynamic loading up to 5 Hz either and can apply loading via cyclic or non-cyclic ‘waves’.

Triaxial
A GDS ‘traditional’ triaxial with both unsaturated soil response and small strain stiffness measurement capabilities.
A triaxial that can act in the ‘traditional’ format (38 mm and 50 mm diameter samples), but by changing the pedestal this instrument can be used to investigate:
- unsaturated response using the HKUST method
- or utilise bender elements to monitor changing stiffness with deformation
Local strain measurement options is also available using a Hall effect transducer (mounted on the sample within the triaxial cell).

Shear box
Small shear box (100mm x 100mm) has back pressure and bender element options for a more refined control/understanding of the shearing behaviour soils.

Automatic oedometer
A pair of GDS automatic oedometers with stepped loading for 38mm, 50mm and 75 mm diameter samples.

Oedometer with confining pressure control
A GDS constant rate of strain oedometer with confining pressure control and pore water pressure measurement. This provides us with an improved understanding of effective stress conditions within the sample.

Soil-water suction
A HYPROP and WP4c from Decagon Devices for measurement of the full range of the soil water characteristic curve, improving understanding of the engineering behaviour of unsaturated soils.

Material Preparation Lab
Material Preparation Lab
GPR Duo & Stream C
Two different ground penetrating radar (GPR) instruments (IDS Duo and IDS Stream C), used to map buried targets. The differing antenna frequencies of the sensors change the investigation depth and spatial resolution of resolvable targets. We also have available two Utsi Electronics 1.5GHz and 4GHz radar suitable for detecting smaller targets buried very shallow.


Scintrex
Two Scintrex CG6 relative gravimeters based on a mass on a spring principle. They can be stacked in gradiometer configuration using the trident stand.

Wee-g
A MEMS gravimeter developed by the University of Glasgow as part of the Quantum Technology Hub in Sensors and Timing.

Magnetometer
A Bartington Grad13 three-axis fluxgate magnetometer capable of detecting small magnetic fields from buried ferrous metal targets. The three axis sensors can be used to accurately locate targets from the strength and direction of the magnetic field and the instrument measures both total fields and magnetic gradients.

Total Stations (Leica & Trimble)
Two surveying total stations are available capable of accurate distance and angle measurements which are used for precise 3D positional mapping of surveys and experiment setups. The Trimble SX10 is also capable of performing high density laser scanning of terrain, buildings and other features to produce 3D point clouds and surfaces.

Tracked Platform
An 800mm wide and 420mm high tracked carrier with a 1200kg capacity. The compact carrier can easily pass through areas with restricted access. It is radio remote controlled and with independently controlled tracks, allows for optimum control, manoeuvrability.

Optical fibre systems (LUNA OBR and ODiSI)
Two multichannel high definition distributed optical fibre systems used to monitor strains (or temperature) when attached to structures or structural components. A typical resolution for larger infrastructure monitoring is strain measurements every 10 mm. along the fibre. The OBR system is a static system capable of monitoring strains at discrete load stages. The ODiSI system is cable of capturing dynamic (real time) changes in strain, for example when the strains are constantly changing during a loading sequence.

GOM
GOM uses digital image correlation through high-speed cameras to allow computation of 2D or 3D coordinates from a series of recorded images. By performing image acquisition over a period of time displacements, velocities, and accelerations are derived from local deformations thanks to a unique identification of the applied pattern. From local displacements, strain elongations and shortenings can be calculated. Hence, this system replaces LVDTs, strain and displacement gauges, and accelerometers all within one kit.

Test Hall
Test Hall
Pit
The pit is 25m by 10m by 5m deep. It can be split into smaller areas using legato blocks. The centre section has a moveable floor. The frame allows surface loading to be applied; One of the end walls of the pit is a strong wall with integrated fixing points allowing jacking operations and horizontal loading to be applied.

Crane
A 20t capacity travelling crane which covers the main test hall.

Centrifuge
This geotechnical beam centrifuge (sample size of 300mm in length, 180mm height and 100mm wide) allows the testing of scale models of geotechnical engineering systems. The sample are spun (rotational speeds of 10 to 638 rpm) to increase g forces and simulate stress experienced in the prototype. The unit is equipped with a two-dimensional actuator, a tunnel system, a cone penetration test (CPT) and particle image velocimetry (PIV) as well as various sensors.

Large Shear Box
Large automated GDS direct shear box can test soil samples with larger sized particles, such as materials used for road and rail construction.

Steel Frame
Steel sections can be used to erect steel frames on the strong floor of the test hall. The flexibility of the sections allows for different configurations to be set up. This allows structural testing of specimens or setting up soil boxes for smaller scale testing compared to the main pit.

Legato Block walls
Legato blocks, of varying sizes, although most are X, Y Z. These are used to build walls in the pit to separate the pit areas into smaller sections. These allow the main pit area to be used flexibly.

Actuators
There are a range of hydraulic actuators for loading the ground or structures:
- 200 tonne (static)
- 50 tonne (static)
- 10 tonne (static)
- 4 x 25 tonne (static or dynamic up to 10 Hz)

Pipeloop
Two pipe loops, internal and external. The external pipe loop is approximately 70m long with a 100mm MDPE pipe buried at approximately 1m below the ground surface. It allows water flow with a pressure of up to 8 bar. It has three large access chambers which allow access to the full circumference of the pipe. An internal pipe network can be constructed in the pit, with the connections capped at the side of the pit. The maximum pressure is 6 bar.
Moveable Floor
The moveable floor comprising 50 actuators allows the simulation of 'ground movements such as those resulting from tunnelling operations or ground heave. Each actuator has a maximum travel of 300mm with 150mm in either direction.

Environmental Chamber
A demountable environmental chamber can sit on the surface of the ground in the pit and provide controllable ambient conditions to an area up to 8.5 m by 4.5 m in plan.
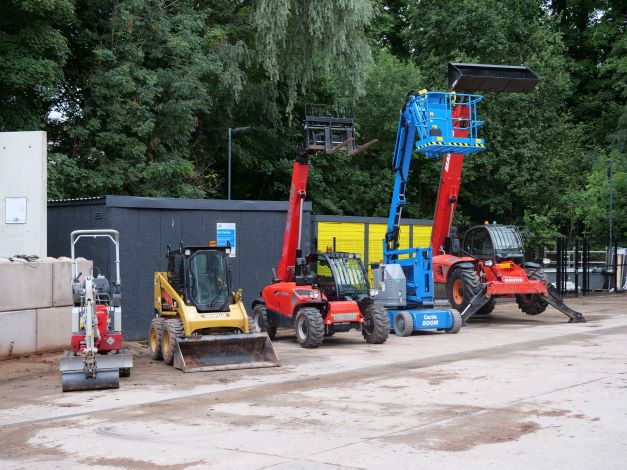
Construction Plant
Construction Plant
A fleet of construction plant is available.
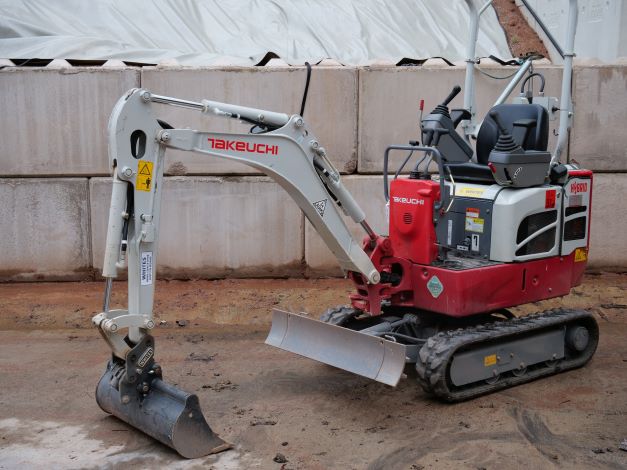
Mini-excavator
Mini-excavator capable of running on both diesel and electric to minimise the fumes in the pit.
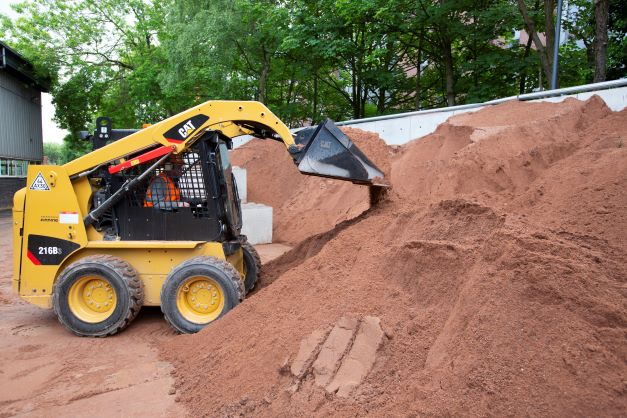
Skid Steer
Small skid-steer used to move sand around. The short wheel spacing provides it with excellent manoeuvrability.
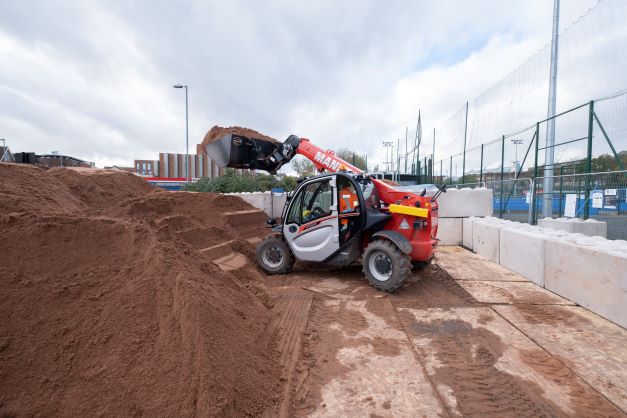
Small Telehandler
Compact sized Manitou telehandler with a maximum lifting weight of 2500kg and a maximum lifting height of 5850mm.

Ariel Boom
Articulated ariel boom capable of lifting two people to a height of 11m.
Large Telehandler
Large Manitou telehandler has a 13.08m horizontal reach, with a maximum lifting weight of 4000 kg and a maximum lifting height of 17.55m.


